Real Time Collaboration¶
Note
To activate Real-Time Collaboration in JupyterLab, is necessary to use Jupyter Server v2.
From JupyterLab 3.1, file documents and notebooks have collaborative
editing using the Yjs shared editing framework.
Editors are not collaborative by default; to activate it, start JupyterLab
with the --collaborative flag and you need to upgrade Jupyter Server to
version 2.0.0 or later. To install it with pip for example:
python -m pip install "jupyter_server>=2.0.0"
To share a document with other users, you can copy the URL and send it, or you can install a helpful extension called jupyterlab-link-share that might help to share the link including the token.
The new collaborative editing feature enables collaboration in real-time between multiple clients without user roles. When sharing the URL of a document to other users, they will have access to the same environment you are working on (they can e.g. write and execute the cells of a notebook).
Moreover, you can see the cursors from other users with an anonymous username, a username that will disappear in a few seconds to make room for what is essential, the document’s content.
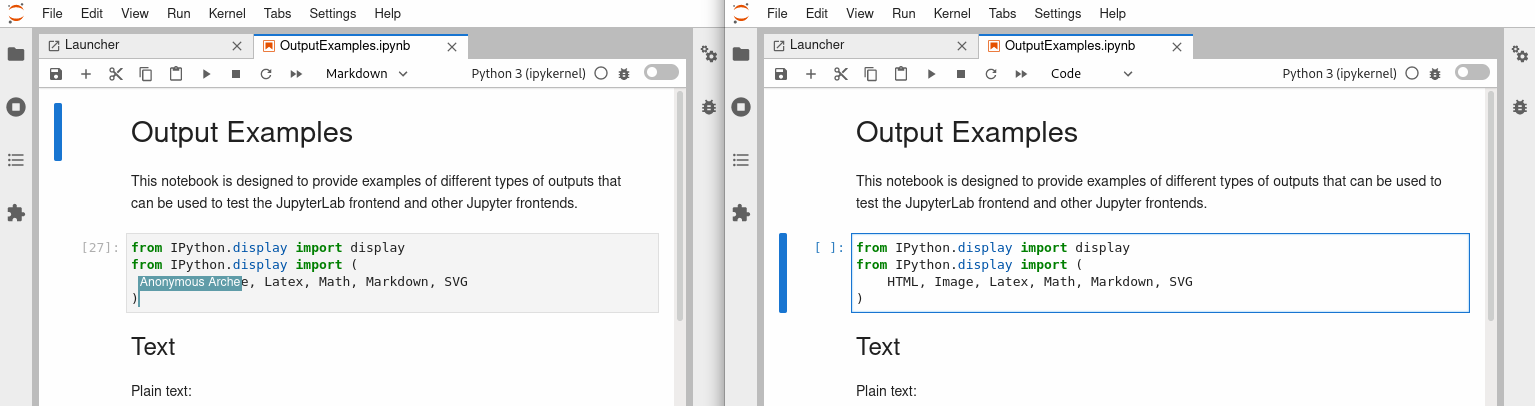
A nice improvement from Real Time Collaboration (RTC) is that you don’t need to worry
about saving a document anymore. It is automatically taken care of: each change made by
any user to a document is saved after one second by default. You can see it with the dirty indicator
being set after a change, and cleared after saving. This even works if the file is modified
outside of JupyterLab’s editor, for instance in the back-end with a third-party editor or
after changing branch in a version control system such as git. In this case, the file is
watched and any change will trigger the document update within the next second, by default.
Something you need to be aware of is that not all editors in JupyterLab support RTC
synchronization. Additionally, opening the same underlying document using different editor
types currently results in a different type of synchronization.
For example, in JupyterLab, you can open a Notebook using the Notebook
editor or a plain text editor, the so-called Editor. Those editors are
not synchronized through RTC because, under the hood, they use a different model to
represent the document’s content, what we call DocumentModel. If you
modify a Notebook with one editor, it will update the content in the other editor within
one second, going through the file change detection mentioned above.
Overall, document write access is much more streamlined with RTC. You will never see any warning message indicating that the file was modified by someone else, and asking if you want to keep your changes or revert to the saved content. There cannot be any conflict, everyone works in sync on the same document.
Note
By default, any change made to a document is saved to disk in an SQLite database file called
.jupyter_ystore.db in the directory where JupyterLab was launched. This file helps in
preserving the timeline of documents, for instance between JupyterLab sessions, or when a user
looses connection and goes offline for a while. You should never have to touch it, and it is
fine to just ignore it, including in your version control system (don’t commit this file). If
you happen to delete it, there shouldn’t be any serious consequence either.
There are a number of settings that you can change:
# The delay of inactivity (in seconds) after which a document is saved to disk (default: 1).
# If None, the document will never be saved.
jupyter lab --collaborative --YDocExtension.document_save_delay=0.5
# The period (in seconds) to check for file changes on disk (default: 1).
# If 0, file changes will only be checked when saving.
jupyter lab --collaborative --YDocExtension.file_poll_interval=2
# The delay (in seconds) to keep a document in memory in the back-end after all clients disconnect (default: 60).
# If None, the document will be kept in memory forever.
jupyter lab --collaborative --YDocExtension.document_cleanup_delay=100
# The YStore class to use for storing Y updates (default: JupyterSQLiteYStore).
jupyter lab --collaborative --YDocExtension.ystore_class=ypy_websocket.ystore.TempFileYStore